The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has become a significant consideration for website owners. In this article, we will explore 12 essential best practices that can help streamline your website’s journey towards GDPR compliance.
By implementing these practices, you can ensure that your website meets the necessary requirements and safeguards user data in accordance with GDPR guidelines. Let’s dive into the top strategies for maintaining GDPR compliance on your website.
Table of Contents
What is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a data protection and privacy regulation passed by the EU Parliament for EU individuals. It came into force on May 25, 2018.
The intent of enforcing the GDPR is to protect people’s data and privacy against breaches and to ensure a safe data-sharing practice.
It applies to any organization or body (worldwide) if it collects and uses the personal data of people in the EU region. In the case of a website, if you receive traffic from the EU region and collect their data, you are liable to comply with GDPR.
As per the GDPR, ‘personal data’ is any information that can be used to identify a living person, with or without additional information. E.g. name, address, email address, bank account details, location identifiers. ‘Sensitive personal data’ refers to the type of personal data of a person that pertains to:
- racial or ethnic origin
- political opinions
- religious or philosophical beliefs
- trade union membership
- genetic data
- biometric data
- health
- sex life
- sexual orientation
Such data require special care and protection.
The GDPR sets out various standards for processing the personal data of the users. In addition to that, it provides several rights for people and lets them have more control over how organizations process their data.
Read the full text here.
Why is the GDPR necessary?
The non-compliance may result in harsh fines that could go up to millions. Or you may also face strict actions that could adversely affect your business.
However, if you think GDPR’s aim is to punish organizations for infringements, then you could not be more wrong. As I have already discussed, the GDPR is a step towards making data sharing and processing safe. Penalties and fines for violations are just a part of it.
GDPR compliance means that you have taken the right steps to protect your website users’ (customers and visitors) data and privacy. You are growing your website’s worth with their trust.
Best practices for your website GDPR compliance
Here are 12 best practices you can follow to make your website GDPR compliant.
#1. Identify the lawful basis
The GDPR lays down six lawful bases for processing personal data, namely:
- Explicit user consent
- To fulfill a contractual obligation
- Legal obligation to process
- Public interest or task
- For a person’s vital interest
- Legitimate interest
You must have clarity about the exact basis for processing the personal data of users on your website. A lot of the data processing activities rely on the purpose of the website.
In most cases of websites, obtaining explicit consent is the lawful basis for processing personal data. At any point where a website requires collecting personal data, the users’ consent is mandatory.
The GDPR defines consent as ‘freely given,’ ‘specific,’ and ‘unambiguous.’ In short, do not force or trick them into consenting with non-negotiable terms and conditions. Let the users give their consent using a clear opt-in method with distinct options for different purposes.
The GDPR also requires websites to enable a clear opt-out option and encourage keeping proof of the consent obtained.
#2. Recognize the risky areas
The GDPR suggests conducting risk assessments or data protection impact assessments to identify high-risk areas, especially if you process sensitive personal data.
Run an analysis on the nature, scope, and purpose of the data processing. Learn its impact on personal data. Then, pinpoint the exact areas that might cause trouble. Identify the appropriate measures to prevent any potential mishaps. Execute each step carefully and seek legal assistance whenever necessary.
#3. The art of keeping a ‘limit’
The GDPR principles discuss various practices for the lawful processing of personal data. All of them suggest limiting the collection and further processing of personal data within the defined purpose for lawful and fair processing.
You must ensure to collect or store only the data you need to serve the purpose of processing. It is against the GDPR standard to store the data longer than necessary.
Handling personal data, such as collecting, using, storing, and sharing, more than the necessary limit is a violation of the regulation.
You must inform the users about your data processing activities and guarantee compliance with the law.

#4. Consent for storing cookies
You already know the conditions for consent under the GDPR. It is nearly impossible for a website owner to not be aware of what cookies are. Websites require cookies to run smoothly and have additional features related to your business.
Some cookies do not store any data. They act as support for the website, without which it may not function properly. Such cookies are harmless and do not require any privacy scrutiny.
However, there are types of cookies that collect personal data for analytics or marketing purposes. Such cookies are often stored by third-party applications you have installed on your website. You must obtain users’ consent before storing such cookies on their devices.
After you identify the type of cookies on your website, you must work on getting the user consent for storing those cookies.
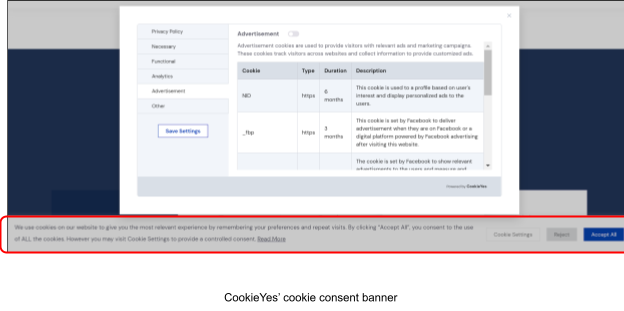
Display a cookie consent popup or banner when the users visit your website. These consent notices must include adequate information, such as the purpose of these cookies and an opt-in and opt-out option for them. The opt-in option must offer granularity for different types of cookies. This cookie consent banner must be easily accessible and link to the privacy policy page.
Here is an example of a cookie consent banner on a website, with settings for users to selectively opt-in for cookies:
#5. Avoid pre-checked consent checkboxes for forms
Forms are common on many websites. They are used for surveys, contact information, subscriptions, account creation, and payment information.
Forms collect user data for these purposes. As per the GDPR, you must obtain user consent to do so.
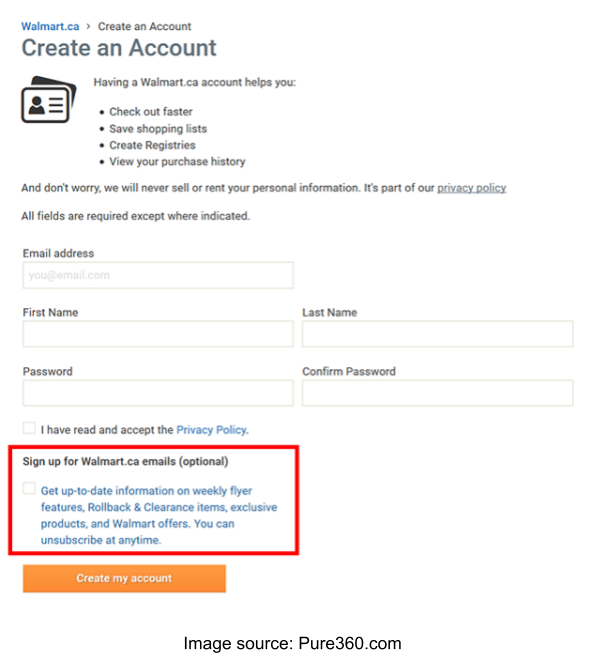
The common method in forms to ask for consent is via checkboxes. You must ensure these checkboxes are not pre-ticked. Using pre-ticked checkboxes for consent is a major violation of the law. You cannot ‘imply’ consent via such methods.
Here is an example from Walmart:
#6. Double opt-in for email subscriptions
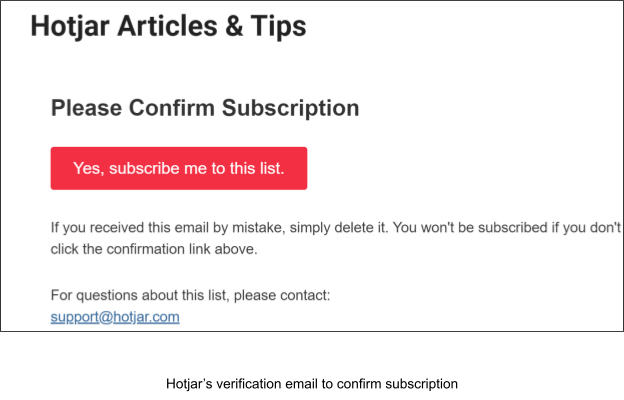
The double opt-in method for subscribing to emails is quite common these days.
It is a method of sending a verification link to the users’ email addresses after they sign up for email marketing or website newsletters.
Such a method avoids any ambiguity regarding the subscription confirmation and follows the GDPR condition for consent.
Every marketing email you send to the users must have an unsubscription or opt-out link or option they can use to withdraw their consent at any time.
#7. GDPR-ready applications
You might have to use third-party applications for enhancing and fine-tuning your website for your intended purpose. These applications may be a great source of trouble if you do not review their policy and data protection practices.
Every time you choose such applications, you must ensure that they follow the necessary GDPR standards to protect the data they collect through your website and share them between both parties.
#8. Provisions for exercising GDPR user rights
One of the, if not the best, provisions that the General Data Protection Regulation has for the people is data rights. These rights make the regulation user-centric and safeguard their privacy.
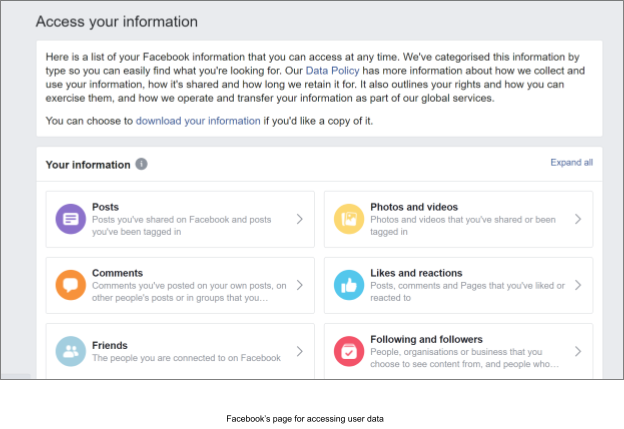
You must make available provisions for the users to exercise these rights at their convenience. You can incorporate a system that responds to t]such requests on time and duly processes them.
For example, users must be able to download a copy of their data stored on the website. Or, there should be an option to delete or place a request to delete or transfer data.
#9. Update the website policy page
One can say that a website is incomplete without a Privacy Policy page. The different data protection legislation in the world has made sure it remains a truth. The GDPR makes no exception to it either. It does not explicitly mention the use of the privacy policy. However, it mandates organizations to practice transparency by sharing necessary information related to data processing with the users.
The privacy policy page is a legal statement on a website that discloses its data processing activities to the users. It must disclose what and how the website collects, uses, stores, protects, and shares personal information. It must also inform how the users can exercise their rights with the necessary contact information.
The GDPR maintains that such disclosure must be easy to understand and easily accessible to the users. You must provide a link to the privacy policy on the homepage of your website.
You can add Information about cookies to the privacy policy. Or, you can also add a separate page, named Cookie Policy. You can share details about how you use cookies on the website on this page.
You can take the help of free privacy policy generator tools to create a policy page for your website.
#10. Secure the website data flow
A website without security is dangerous. So many websites have fallen prey to hackers. Therefore, you must install security systems on the website for the entire process flow.
You must adopt the Privacy by Design approach that proposes implementing security measures from the designing process of the website. Every entry point, such as login, to the exit point of the website must be secured and shielded using technical measures.
Some of the commonly used techniques are:
- Data encryption
- SSL certification
- IP anonymization
- Anti-malware firewall
- Limited login attempts
- Strong passwords with two-way authorization
- Remote backup (while respecting GDPR norms)
- ReCaptcha technique
#11. Data breach response system
Another best practice is to be prepared for events like data breaches. Your system must always be ready with a fast action and response plan to mitigate the loss from data breaches.
You must be able to immediately notify your local supervisory authority and the affected users, within 72 hours of identifying the breach.
It would be beneficial to have a template ready for the data breach report. It must explain what data was affected; the severity of the breach; what you have done to mitigate it; and the advice for the users to protect their data.
#12. Document everything
It is a no-brainer that documenting all the data activity processes and your actions will help you in the future.
Logging the details will be a great resource for reviewing your performance and taking better measures for compliance.
Closing thoughts
I hope you will find these best practices helpful. It may not guarantee a fully GDPR-compliant website, but it will ensure that you are on the right path for it.
I would advise you to take legal assistance wherever necessary to not miss out on any crucial details.
Also, it is advisable to refer to powerful tools to optimize your website.


